Relativistic Jets from AGNs
What properties of relativistic jets can we infer through broadband SED modeling?
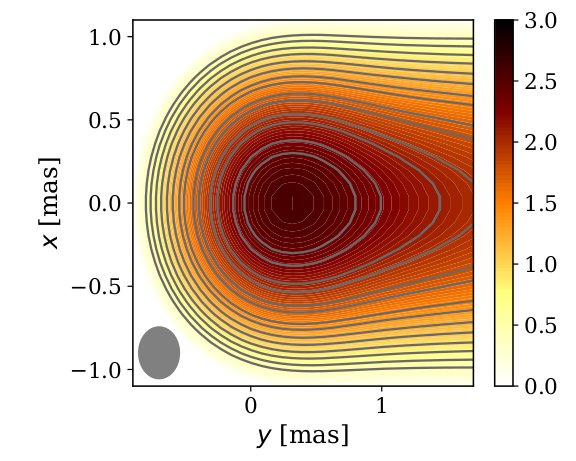
Relativistic jets are collimated outflows of plasma launched from the vicinity of accreting compact objects. These jets can extend over distances of Mpc and are among the most powerful persistent phenomena in the Universe. In active galactic nuclei (AGN), jets are responsible for a significant fraction of the observed emission across the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to gamma rays.
Understanding the composition, structure, and emission mechanisms of these jets is fundamental to unraveling the physics of accretion and outflow in extreme environments. The broadband spectral energy distribution (SED) of relativistic jets encodes information about the particle populations, magnetic field strength, and geometry of the emitting regions. Through detailed modeling of the observed SEDs, we can constrain key physical parameters such as the jet power, bulk Lorentz factor, and the properties of the accelerated particle distributions. I have worked on understanding both the radiative processes in jets and the fundamental question of how jets are loaded with matter in the first place.
In (Romero & Gutiérrez, 2020), I investigated the origin of matter at the base of relativistic jets in AGN. We analyzed various mechanisms through which jets can be loaded with leptons and baryons, including processes occurring in the hot accretion flow surrounding the black hole. Understanding jet composition is crucial because it determines the jet's dynamics, stability, and ultimately its radiative properties.
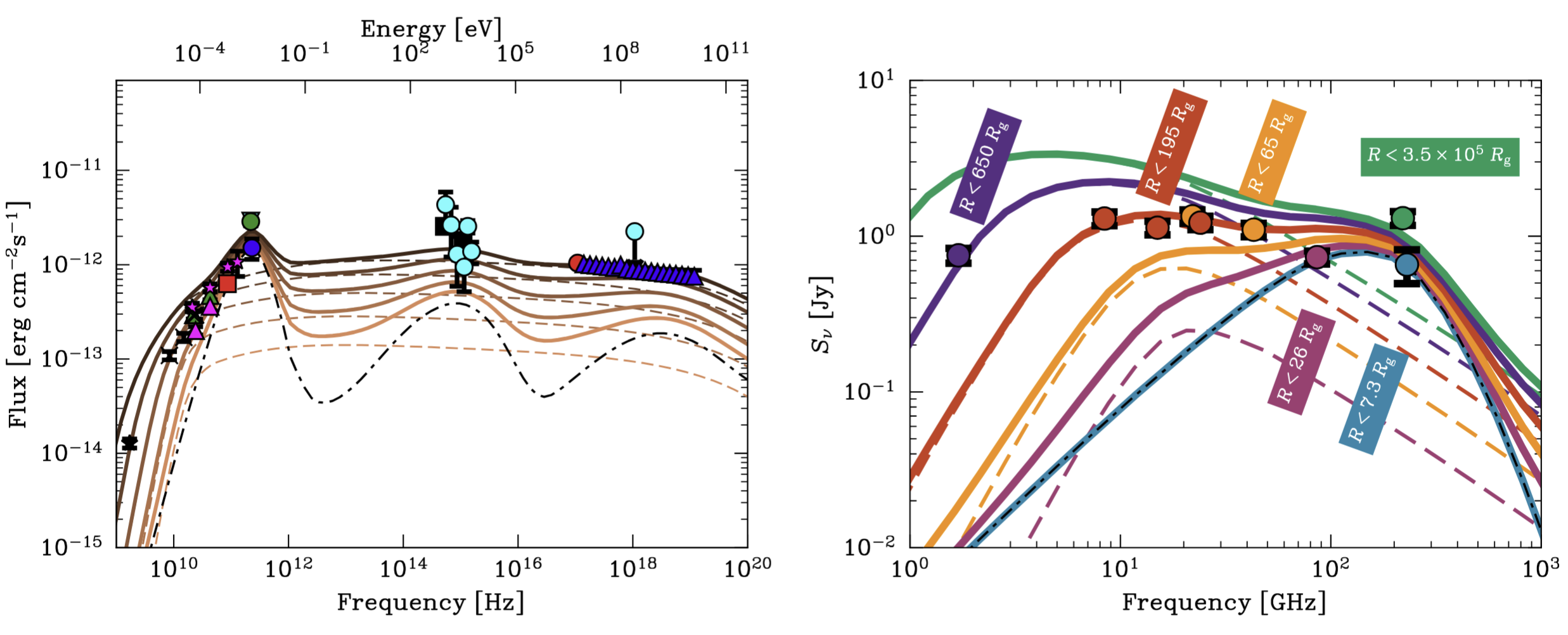
With my master student, Tomás Mazzei, we are currently finishing a work on a multizone modeling of M87 and Centaurus A accretion/jet systems, explaining the high-resolution radio observations of these sources on different spatial scales, with a special focus on the latest Event Horizon Telescope observations.
References
2020
- The Origin of Matter at the Base of Relativistic Jets in Active Galactic NucleiUniverse, 6(7), Jul 2020